
Phimask - A Phase Mask to Turn a 2D SMLM Setup Into a 3D Image - PBO-SEL
- Regular price
- $6,648.25 USD
- Regular price
-
- Sale price
- $6,648.25 USD Sale
- Unit price
- /per
- Availability
- Sold out
Adding product to your cart
Phimask is a diffraction grating system made for tracking native cellular processes in intact tissues with the following features:
- Compatible with up to 3 colors in the 500-750nm range
- Generating interferences with <20% photon loss
Size: 1 Unit (PBO-SEL)
Phimask is a super resolution imaging tool for turning a 2D SMLM setup into a 3D image. This phase mask is meant for bioimaging analysis to track native cellular processes in intact tissues using phase encoded-positioning. It can be adapted to any microscope.
Adding Phimask to the experiment
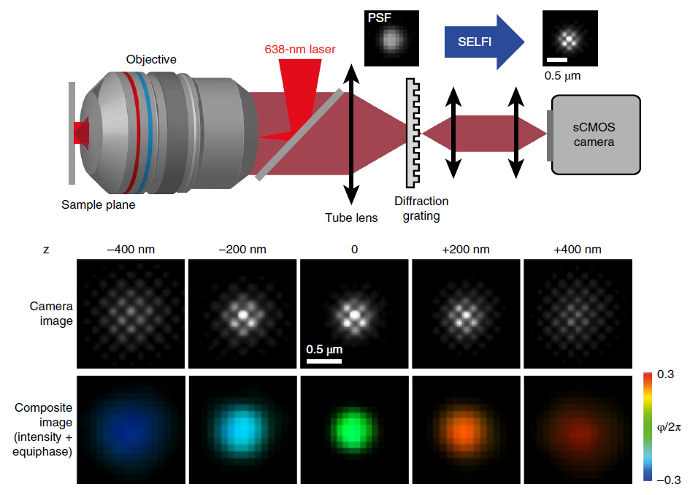
The PhiMask has to be placed a in front of the sensor of the camera you want to use. If the sensor is mechanically inaccessible, you can use an imaging relay.
The Phimask produces interferences (fringes) which are sampled by your camera. The fringes carry the particule localization in 3D.
Retrieving the 3D localization
By using fluorescent smaller than the resolution of the microscope (e.g. 100 nm beads for a NA=1.4 microscope objective) and a z-axis motorized microscope, it is possible to perform a calibration of the SELFI-PSF along the z axis. This calibration can be used as a look-up-table to determine the axial z localization of each emitter during an experiment.
The lateral localization can be obtained by applying a low-pass filter to the image to remove the fringe modulation. This leads to the signal envelope which is exactly the same as recording the image with the PhiMask; regular state-of-the-art 2D localization algorithms can be applied (ex. 2D Gaussian fitting, Wavelets...).
Results
This is a 3D super-resolution design that was published in Bon et al. Nat. Methods 2018. In the image below, you can see that you just have to position the diffraction grating, PhiMask, between the tube lens and the CMOS camera. PhiMask is doing self-interference that change PSF into sub PSF-structuration with very limited photon-loss (less than 20%).
When you have the single-emitter information with sub-PSF structuration, you can simultaneously extract the position in XY and Z.
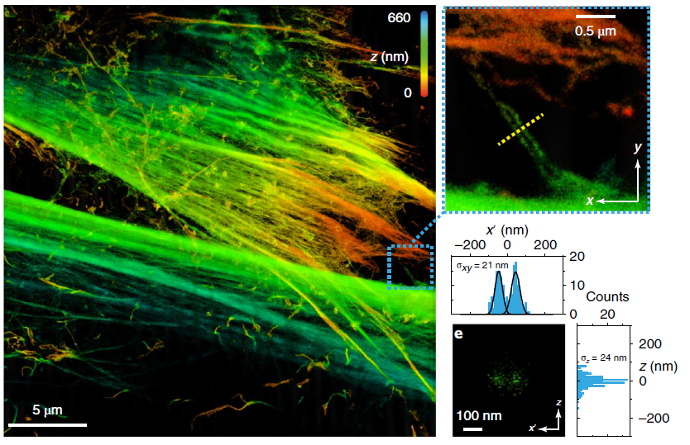
Nanoscale Architecture of Cytoskeletal and Adhesion Networks
Description: Super-resolution imaging reveals aligned filamentous structures with nanoscale spatial organization, highlighting the coordinated arrangement of cytoskeletal elements and associated adhesion components across the cell. The data demonstrate pronounced structural anisotropy and localized clustering at submicron length scales.
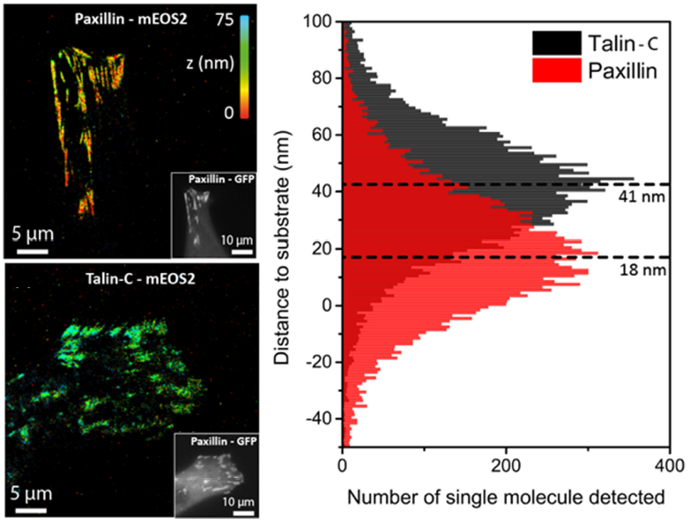
Distinct Axial Localization of Talin and Paxillin in Focal Adhesions
Description: Single-molecule localization analysis shows that talin and paxillin occupy separable vertical layers within focal adhesions. Talin is positioned higher above the substrate than paxillin, indicating a stratified molecular organization consistent with their distinct mechanical and signaling roles.
More information can be found on the Datasheet.