Magnetofectamine™ O2 is the new powerful and ideal transfection kit designed for primary and hard-to-transfect cells. The alliance of MTX transfection reagent and CombiMag leads to increased transfection efficiency, minimized toxicity and enhanced gene expression.
This kit replaces and outperforms the original Magnetofectamine™ which was the combination of Lipofectamine™* 2000 from Life Technologies Corporation and CombiMag Transfection Reagent.
CombiMag, a magnetic formulation based on the Magnetofection™ technology, binds to MTX transfection reagent/DNA complexes and under the application of a magnetic field concentrates the genetic material onto cells and promotes cellular uptake. In this way, transfection efficiency is enhanced.
- Less nucleic acids used - minimized toxicity
- No need to change your standard protocol
- Ideal for hard-to-transfect and primary cells
- Simple, ready-to use and rapid
- Serum compatible and applicable to all nucleic acids
Magnetofectamine O2 Transfection Kit for Primary Cells
Sizes :- MTX2-1000 Starting Kit: 1 super Magnetic Plate (MF1000) + 250 µL CombiMag + 750 µL MTX reagent + 3 ml MTX Boost 100X
- MTX2-0750: 250 µL CombiMag + 750 µL MTX reagent + 3 ml MTX Boost 100X
- This reagent needs to be used with a magnetic plate
Applications
Magnetofectamine O2 Transfection Kit for Primary Cells
- Boost transfection efficiency with reduced cell toxicity
- Ideal for mammalian cells: Cell lines, primary & hard to transfect cells.
- Perfect for all transfections: Transient, stable, gene silencing, with or without serum
- Suitable for all nucleic acids: DNA, oligonucleotides, mRNA, siRNA, shRNA
RECOMMENDED FOR: Transfection of primary and hard-to-transfect adherent cells
Results
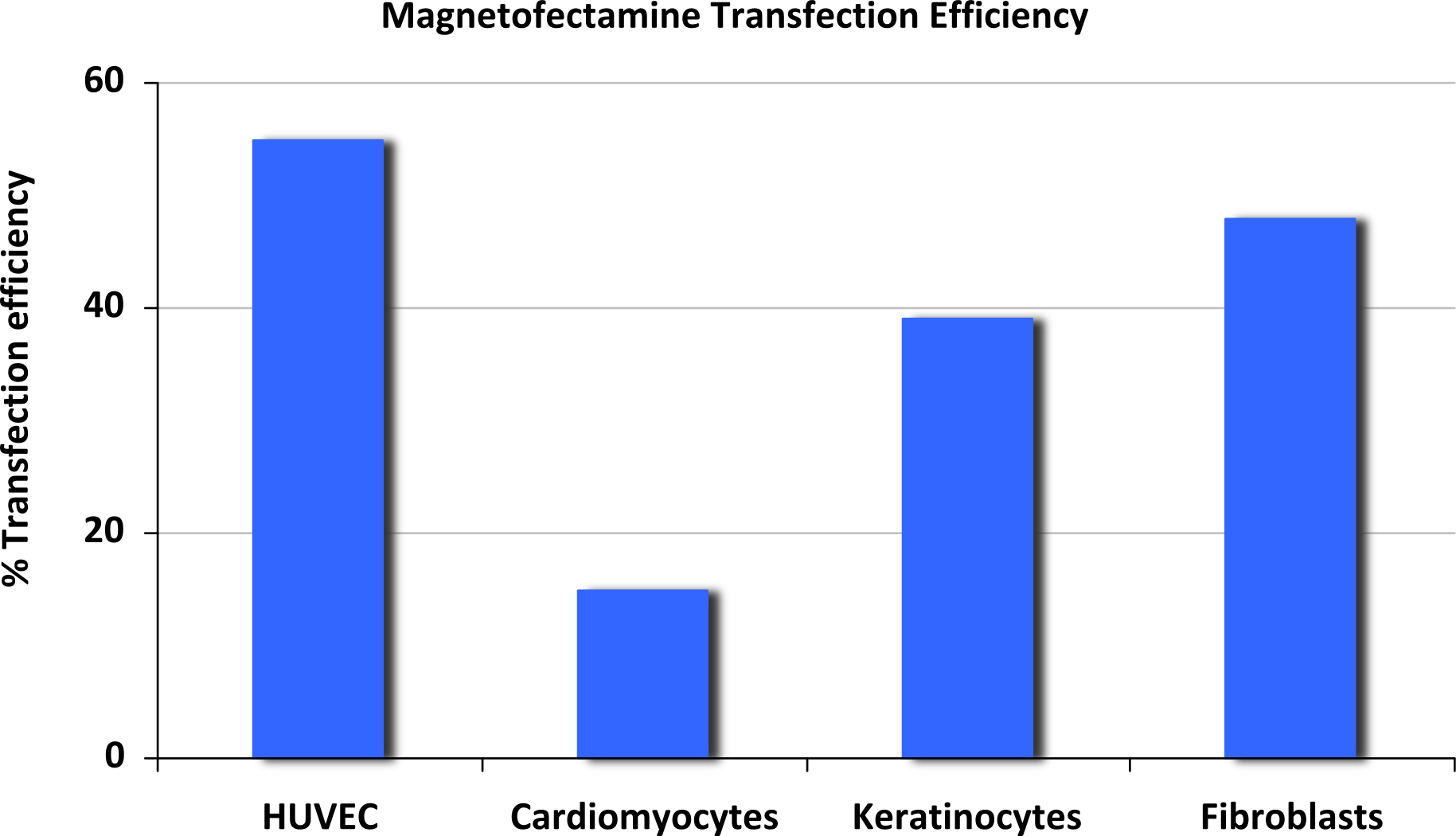
Figure 1: Magnetofectamine O2 transfection efficiency.
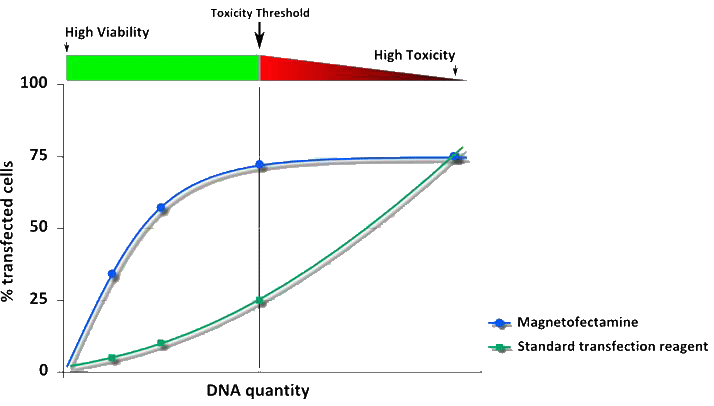
Figure 2: As the magnetic force drives the gene vector towards the target cells, Magnetofectamine™ O2 allows the vector dose to concentrate onto the cell very rapidly and triggers delivery via endocytosis. Consequently, high transfection efficiencies can be achieved with less nucleic acid amount.





